Bi-directional Contrastive Learning for Domain
Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
ECCV 2022
Abstract
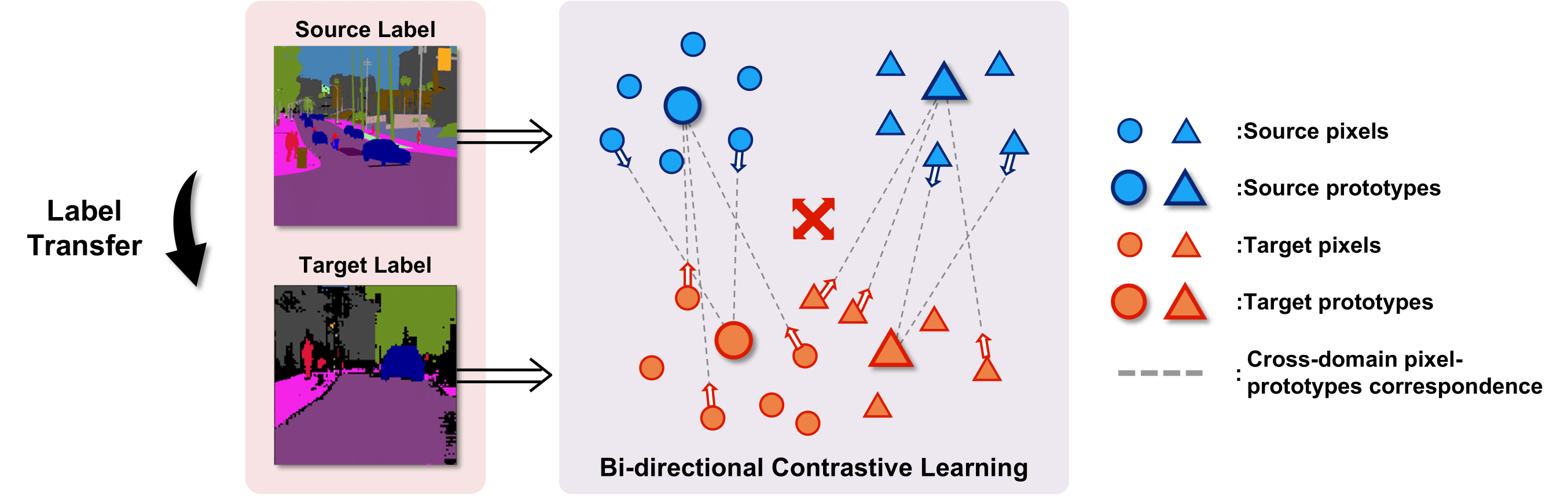
We present a novel unsupervised domain adaptation method for semantic segmentation that generalizes a model trained with source images and corresponding ground-truth labels to a target domain. A key to domain adaptive semantic segmentation is to learn domain-invariant and discriminative features without target ground-truth labels. To this end, we propose a bi-directional pixel-prototype contrastive learning framework that minimizes intra-class variations of features for the same object class, while maximizing inter-class variations for different ones, regardless of domains. Specifically, our framework aligns pixel-level features and a prototype of the same object class in target and source images (i.e., positive pairs), respectively, sets them apart for different classes (i.e., negative pairs), and performs the alignment and separation processes toward the other direction with pixel-level features in the source image and a prototype in the target image. The cross-domain matching encourages domain-invariant feature representations, while the bidirectional pixel-prototype correspondences aggregate features for the same object class, providing discriminative features. To establish training pairs for contrastive learning, we propose to generate dynamic pseudo labels of target images using a non-parametric label transfer, that is, pixel-prototype correspondences across different domains. We also present a calibration method compensating class-wise domain biases of prototypes gradually during training.
Approach
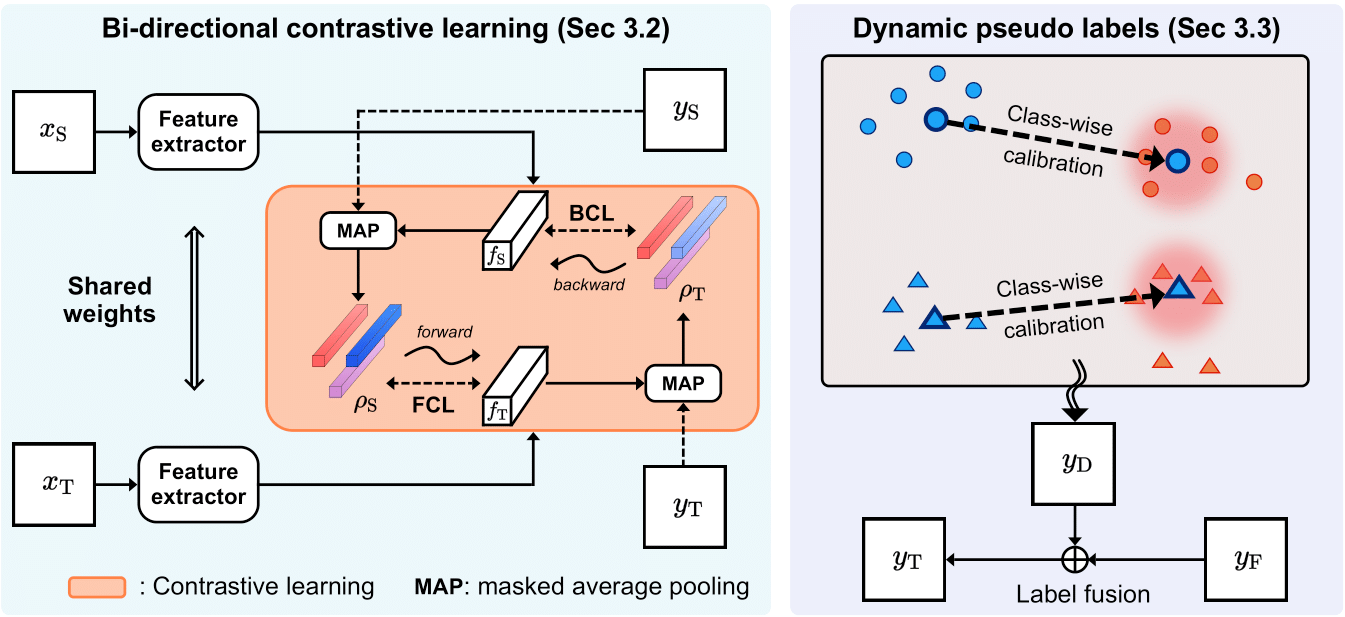
An overview of our framework.
(Left) Bi-directional contrastive learning: We first extract feature maps, from source and target images, respectively. We then obtain prototypes in a source domain using ground-truth labels of source images . Prototypes in a target domain are similarly computed but with dynamic pseudo labels of target images. Bidirectional contrastive terms, FCL and BCL, exploit pixel-prototype correspondences across domains to learn domain-invariant and discriminative features for UDASS. (Right) Hybrid pseudo labels: We generate dynamic pseudo labels using pixel-prototype correspondences across domains, while calibrating the prototypes to reduce domain discrepancies. We then combine them with static ones using a parametric approach to obtain hybrid pseudo labels.
Paper
|
G. Lee, C. Eom, W. Lee, H. Park, B. Ham Bi-directional Contrastive Learning for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation In Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2022 [ArXiv] [Code] [Bibtex] |
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Institue of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea goverment(MSIT) (No.RS-2022-00143524, Development of Fundamental Technology and Integrated Solution for Next-generation Automatic Artificial Intelligence System, and No.2022-0-00124, Development of Artificial Intelligence Technology for Self-Improving Competency-Aware Learning Capabilities), and the Yonsei Signature Research Cluster Program of 2022 (2022-22-0002).